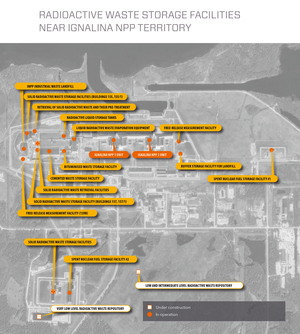
Radioactive waste management facilities
Radioactive waste management facilities are installations for the management of radioactive waste: waste treatment facilities, storage facilities and repositories.
In Lithuania, all radioactive waste management facilities are located near the Ignalina NPP in the territory of Visaginas Municipality, except for the closed Maišiagala Radioactive Waste Storage Facility in Širvintos district.
Click on the image for a larger view
Depending on the risk to people and the environment radioactive waste is divided into very low level, low and intermediate-level and high level radioactive waste, and short-lived and long-lived according to the half-life of radionuclides and they are managed in different facilities.
Find more in infographic “What is radioactive waste?“
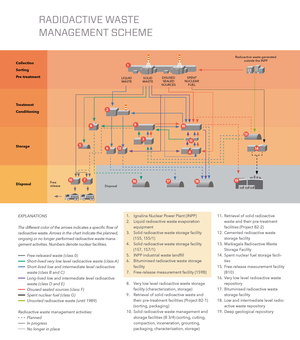
Below you can find a scheme showing the steps and methods of radioactive waste management in Lithuania and descriptions of the radioactive waste management facilities.
Click on the image for a larger view
Spent nuclear fuel and long-lived radioactive waste treatment facilities
Short-lived low and intermediate-level radioactive waste treatment facilities
Very low-level radioactive waste treatment facilities
Free release measurement facilities
Spent nuclear fuel and long-lived radioactive waste treatment facilities
Spent nuclear fuel storage facilities
Solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities
Retrieval of solid radioactive waste from buildings 157 and 157/1 and their pre-treatment facilities
Deep geological repository
Spent nuclear fuel storage facilities
In Lithuania, spent nuclear fuel is not reprocessed, so after unloading it from the Ignalina NPP it is stored for several years in the cooling pools near the reactor and after it is transported in two storage facilities for spent nuclear fuel (SNFSF-1 and SNFSF-2) near the nuclear power plant. Both storage facilities are of the dry-type and the spent fuel is stored in the same containers in which it is transported to the storage facilities.
The first spent fuel storage facility (SFSF-1) was commissioned in 2000. It stores the spent fuel in two special types of containers for the storage of spent fuel from RBMK reactor: the CASTOR RBMK-1500 (CASTOR) and the CONSTOR RBMK-1500 (CONSTOR). The CASTOR containers are 4.3 m of height and 2,072 m in diameter, together with the spent fuel each container weighs 71.84 tons. The CONSTOR containers are 4.7 m high and 2.3 m in diameter, each container together with the spent fuel weighs 84.43 tons. This storage facility is fully stocked with a total of 20 CASTOR and 98 CONSTOR containers with 6018 spent fuel assemblies.
The second spent fuel storage facility (SFSF-2) was put into operation in 2017. Spent nuclear fuel in this facility is stored in a new type containers CONSTOR RBMK-1500/М2. Each of them is 4.5 m height and 2.6 m in diameter and 118 tons of weight. After interim storage period (up to 50 years) all spent fuel will have to be disposed of in a deep geological repository.
At the beginning of 2023, the Ignalina NPP has no nuclear fuel left in its power units, and all spent and unspent nuclear fuel has been transferred to SFSF-2. In total 190 containers containing spent nuclear fuel are stored in the storage facility (including 22 ones containing damaged fuel), plus one extra empty container for the reloading of spent fuel in the storage facility’s hot cell in case a spent fuel container is no longer leak-tight. There are also 8 special metal containers containing unspent nuclear fuel.
Solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities
Solid radioactive waste generated during Ignalina NPP operation and decommissioning is stored in the old Ignalina NPP storage facilities (buildings 155, 155/1 and 157, 157/1). In order to manage the accumulated waste in compliance with the latest requirements for the radioactive waste management and to modernize the waste management system, it was decided to build a new complex of solid radioactive waste treatment and storage facilities.
The solid radioactive waste previously accumulated and stored in the old storage facilities will be retrieved, re-sorted, treated and placed into the new storage facilities. For this reason special retrieval facilities (projects B2-1 and B2-2) have been designed and built. The waste sorting and treatment facilities installed in the complex will perform functions of receiving, sorting, cutting, compaction, inceneration, packaging, grounting, characterization of the waste and transfer to radioactive waste storage facilities.
Solid radioactive waste accumulated during the operation and decommissioning process of the Ignalina NPP will be managed and stored in these facilities. The long-lived radioactive waste will be cut to fit into the storage containers and stored in a storage facility dedicated for this type of waste for about 50 years. The planed capacity of the long-lived radioactive waste storage facility is about 2000 m3 and it could be extended if necessary up to 8000 m3 by constructing additional modules.
Later, this waste will be disposed of in radioactive waste repositories.
In March 2022, Lithuanian State Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate (VATESI) issued two permits to SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant for industrial operation of solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities.
Retrieval of solid radioactive waste (buildings 157, 157/1) and their pre-treatment facilities
Solid radioactive waste retrieval facilities (Project B2-2) are installed on the roof of old Ignalina NPP storage facilities (buildings 157 and 157/1). Special equipment installed in retrieval facilities will remove long-lived radioactive waste from the old storage buildings. This waste transferred to the newly built solid radioactive waste management and storage facility (Project B3/4) will be re-sorted according to the latest requirements, put into special packages and containers and stored until the deep geological repository is constructed.
The hot trials of the retrieval facilities has started in October 2017.
In June 2020, VATESI approved updated safety justification documents of solid radioactive waste retrieval facilities (Project B2-2) installed on the Ignalina NPP solid radioactive waste storage facilities (buildings 157, 157/1) based on the results of hot trials. This decision of VATESI allowed the start of commercial operation of the facilities.
Deep geological repository
Status: planning stage
The deep repository, which is planned to be built and installed in Lithuania in 2068, is the final disposal facility for spent nuclear fuel and long-lived radioactive waste.
A deep repository is a special engineering facility built several hundred metres underground to contain radionuclides in radioactive waste and to isolate highly radioactive waste from external influences, thus protecting people and the environment from the harmful effects of ionising radiation. The safety of people and the environment is ensured through containment and isolation by natural barriers (deep-seated rocks) and a number of complementary artificial (engineered) barriers.
Stages and the schedule of the implementation of deep geological disposal facility is established in the Nuclear facilities Decommisssioning and Radioactive Waste Management Development Programme, approved by the Government of Lithuania in 2021. The deep repository site investigation programme is expected to be completed in 2047. It is tentatively planned that the deep repository will be constructed in 2058–2067, operated in 2068–2074, and closed in 2075–2079.
SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant is responsible for the implementation of the deep disposal facility project and, together with the Ministry of Energy, it coordinates the disposal facility installation works and periodically updates the schedule of planned works.
More information about disposal facility project.
Short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste management facilities
Cemented radioactive waste storage facility
Retrieval of solid radioactive waste (buildings 155, 155/1, 157/1) and their pre-treatment facilities
Solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities
Short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste repository
Cemented radioactive waste storage facility
The storage facility was put into operation in 2006 and it contains the cemented wastes – concentrate sediment, spent ion-exchange resins from Ignalina NPP water treatment and liquid waste treatment system, filter aid material (perlite).
Cemented radioactive waste storage facility is reinforced concrete structure. The possible storage term of waste packages inside the facility is 60 years. Cement-solidified waste is poured into 200 liter drums, which are placed into a storage container. In total, facility can contain up to 6,300 containers. The volume of one container is about 5.6 m3 and it holds 8 barrels. At the end of 2022, 19,758 packages (drums) containing cemented liquid waste were stored in this facility.
Also a part of Ignalina NPP decommisioning waste (solid radioactive waste) will be stored in this facility after safety assessment. Such assessment already was done for reactor channel graphite waste and agreed with VATESI in 2018. It will be placed in steel drums and put inside the same concrete containers as the cemented waste.
Retrieval of solid radioactive waste (buildings 155, 155/1, 157/1) and their pre-treatment facilities
Status: in commercial operation
Solid radioactive waste retrieval facilities (Project B2-1) are constructed near the old Ignalina NPP storage facilities (buildings 155, 155/1) as extensions of these buildings. These facilities will be used to retrieve short-lived radioactive waste from old storage facilities, re-sort and place it in special packaging.
Waste will be removed via remotely controlled equipment through openings in the walls of the old INPP storage facilities and transferred to the constructed extensions of 155 and 155/1 buildings, where waste will be sorted, characterized and placed in containers. Most of this waste will be transported to a very low level radioactive waste storage facility and later disposed of in a very low level radioactive waste repository. Waste that does not meet the acceptance criteria for this repository will be transported to a newly built solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities, where it will be treated and stored until the repository for short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste is constructed.
One of the solid radioactive waste retrieval facilities (Project B2-2) installed on the roof of old Ignalina NPP storage facilities (buildings 157 and 157/1) are also designated for the retrieval of the short-lived waste from the building 157/1. Retrieved waste will be transferred to the newly built solid radioactive waste management and storage facility (Project B3/4), re-sorted, conditioned and placed to the short-lived radioactive waste storage facility. Later, this waste will be disposed of in repository for short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste.
In April 2019 VATESI issued a permit to SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant for commercial operation of solid radioactive waste removal and pre-treatment facilities (project B2 part 1).
In June 2020, VATESI approved updated safety justification documents of solid radioactive waste retrieval facilities (Project B2-2) installed on the Ignalina NPP solid radioactive waste storage facilities (buildings 157, 157/1) based on the results of hot trials. This decision of VATESI allowed the start of commercial operation of the facilities.
Solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities
Solid radioactive waste generated during Ignalina NPP operation and decommissioning is stored in the old Ignalina NPP storage facilities (buildings 155, 155/1 and 157, 157/1). In order to manage the accumulated waste in compliance with the latest requirements for the radioactive waste management and to modernize the waste management system, it was decided to build a new solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities.
The solid radioactive waste previously accumulated and stored in the old storage facilities will be retrieved, re-sorted, treated and placed into the new storage facilities. For this reason special retrieval facilities (projects B2-1 and B2-2) have been designed and installed.
In the new facility, low-level combustible waste will be incinerated and low-level and medium-level radioactive waste will be compressed to reduce volume of radioactive waste. This way treated waste will be placed in containers. Containers with short-lived intermediate-level radioactive waste will be filled with concrete to prepare radioactive waste packages for disposal in the short-lived low and intermediate level waste repository. Before disposal, these packages will be stored in a short-lived radioactive waste storage facility for approximately 50 years. Most of solid radioactive waste generated during the operation and decommissioning of the Ignalina NPP will be managed and stored in this facility.
In March 2022, Lithuanian State Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate (VATESI) issued two permits to SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant for industrial operation of solid radioactive waste management and storage facilities.
Short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste repository
A near surface repository is a surface repository where natural and artificial (engineering) barriers prevent the spread of radionuclides into the environment. Such repositories need to be maintained for several hundred years (up to 300 years). Later, even after the degradation of engineering barriers, the waste no longer poses a risk.
All short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste currently stored in Ignalina NPP storage facilities and generated during decommissioning will be disposed in a near surface repository (project B25). Near Surface Repository will be built in the territory of Stabatiškė site in Visaginas municipality near other Ignalina NPP radioactive waste management facilities.
The packages transported from the other INPP radioactive waste treatment facilities to the repository will be verified and accepted. Part of radioactive waste (containers with spent ion-exchange resins and large size components) will be conditioned and disposed in the repository. Radioactive waste packages will be placed in concrete vaults (full capacity of 100 000 m3), which after their filling will be covered by clay layer and multilayer cover of layers of silty sand, clay, gravel, rubble, boulders and vegetation. It is intended that the disposal of packages will continue till the end of decommissioning in 2038. Radiological monitoring of repository will be conducted during operational and post-closure periods as well other institutional control measures will be implemented during post-closure period.
VATESI issued a licence to SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant for construction and operation of repository for short-lived low and intermediate level radioactive waste (project B25) in November 2017. Preparatory works for the construction of the repository are ongoing.
Very low level radioactive waste managment facilities
Very low level radioactive waste storage facility
Very low level radioactive waste repository
Very low level radioactive waste storage facility
Very low radioactive waste storage facility (Project B19-1) has been constructed on a territory of Ignalina NPP and being operated since 2013. Facility has special unit for characterization of the packages of radioactive waste (determination of the radionuclide composition) and buffer storage. It contains three type of packages: bundles of compressed solid radioactive waste (waste wrapped in steel strips and polyethylene film), flexible plastic containers (FIBC package) filled with used ion exchange resins in and half-height ISO containers filled with uncompressed solid waste. The intended capacity of the buffer storage is 4000 m³. Later, accumulated waste will be placed into very low level radioactive waste repository.
The planned operational term of the storage facility is about 30 years, until the decontamination and dismantling of buildings and structures at the Ignalina NPP industrial site is completed.
Very low level radioactive waste repository
Repository for very low level radioactive waste is a near-surface disposal facility at ground level for emplacement of waste with no intention of retrieving it in the future. Natural and installed artificial (engineering) barriers ensure that harmful quantities of radioactivity are not released into the environment. Surveillance of the repository must be carried out for at least 100 years after closure. Over this period, the activity of this waste will automatically decrease and become non-hazardous to people and the environment.This landfill-type repository is being constructed in Visaginas municipality, near Ignalina NPP (project B19-2). It will consist of three modules with the capacity of up to 20 000 m³ each.
The packages of very low radioactive waste transported from the other Ignalina NPP radioactive waste treatment facilities will be placed on a reinforced concrete foundation.
It will contain half-height ISO containers with uncompressed solid radioactive waste, plastic bundles with compressed radioactive waste and flexible plastic containers (FIBC package) with spent ion exchange resins. Packaging-filled modules will be covered with a multilayer coating of layers of consisting of sand, gravel, bentonite and high density polyethylene film, gravel and geotextile and topsoil and soil. These barriers will prevent water penetration into the waste stack and washout of radionuclides from the waste to the surrounding environment.
Repository will be completely filled with the radioactive waste packages in about 20 years. After closure, active repository surveillance (radiological and environmental monitoring, physical security) should be carried out for another 30 years. Restriction on land use near repository will remain for next 70 years. Similar disposal faciliites have been already put into operation in Sweden, France and Spain.
In December, 2015 VATESI issued the licence to the State Enterprise Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant authorising the construction and operation of very low-level radioactive waste disposal facility (Project B19-2).
On April 1, 2022 VATESI issued a permit to the State Enterprise Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant for transportation of radioactive waste to the Very low level radioactive waste repository and conduct tests of the repository systems using radioactive waste for the first time.
In November 2023, the SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant completed the second radioactive waste loading campaign.
Free-release measurement facilities
Two free-release measurement facilities are installed in Ignalina NPP (159B and B10 buildings), where intended devices measure whether materials and wastes correspond to the clearance condition by determining the concentration of radionuclides. Depending on the results it is decided, whether materials and waste no longer needs to be controlled from the point of view of radiation protection. These materials can be reused or waste can be treated as ordinary waste. For example, part of the equipment or metal parts can be reused in industry or construction rubble can be treated as ordinary construction waste.
Other waste that exceeds out-of-control levels are decontaminated again, or managed as radioactive waste.
Updated: 29-03-2024