Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant consists oftwo RBMK-1500 type reactors (designed electrical capacity of 1500 MW for each unit). The Unit 1 was commissioned at the end of December 1983, the second Unit 2 in August 1987. The construction of INPP necessitated constructing 142 km of roads, 50 km of railway, 390 km of communication lines, 334 km of electricity lines, 133 km of sewerage lines, and 164 km of thermal lines. Also 3 544000 m³ of concrete and reinforced concrete and 76480 tones of reinforcement was used for the construction.
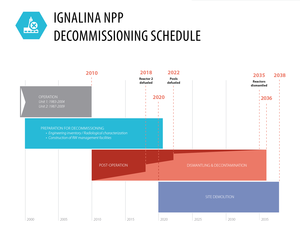
In accordance with the Protocol for Admission of the Republic of Lithuania to the European Union Ignalina NPP Unit 1 was shut down on 31 December 2004 and Unit 2 was shut down on 31 December 2009.
Beside Unit 1 and Unit 2, license for operation of Ignalina NPP covers also radioactive waste treatment and storage facilities initially designed for NPP's operational radioactive waste management:
- Liquid radioactive waste treatment facilities, where liquid waste are evaporated, cleaned using ion-exchange resins and filter aid perlite The evaporatin concentrate is solidified, using bituminization facility and spent ion-exchange resins filter aid (perlite) and part of evaporator concentrate with solid particle sediments are solidified in cementation facility;
- Solid radioactive waste storage facilities (155, 155/1 and 157, 157/1 buildings) where radioactive waste of different activity are stored;
- Ignalina NPP industrial waste landfill containing industrial waste generated during the operation of the units;
- Bituminous waste storage facility (Building 158) containing bituminized waste from liquid radioactive waste processing facilities;
- Free release measurement facility (Building 159B) – it estimates the activity of radionuclides in waste and materials using special dosimetry equipment and verifies compliance with the clearance condition. If concentrations of radionuclides comply with acceptance criteria materials can be reused and waste can be treated as conventional non-radioactive waste.
State Enterprise Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant performs works for decommissioning of Ignalina NPP, including decontamination and dismantling of equipment and buildings, treatment and storage of radioactive waste. At the beginning of 2023, the Ignalina NPP has no nuclear fuel left in its power units, and all spent and unspent nuclear fuel has been transferred to the second spent fuel storage facility (SFSF-2).
Also the bituminous waste storage facility will be upgraded. In 2023, VATESI made decision to approve site safety evaluation report for planned disposal facility of bituminous radioactive waste.
It is expected, that dismantling of the first reactor will start in 2027 and the second reactor in 2029. The decommissioning of the Ignalina NPP is scheduled for 2038.
Click on the image for a larger view
The State Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate (VATESI) carries out supervision of the decommissioning of the Ignalina NPP by issuing and updating various safety requirements, conducting inspections, licensing the decommissioning activities and issuing permits for various works. Although Ignalina NPP is not in operation, its physical security, maintenance of operating systems, accounting of nuclear materials is continually ensured and other works are in progress.
Currently VATESI is evaluating the SE Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant application documents (received on 14 September 2018) for the license for the decommissioning of nuclear facilities.
More information:
Ignalina RBMK-1500. A Source Book
Updated: 29-03-2024